Borehole Geophysical Methods – Seismic Methods
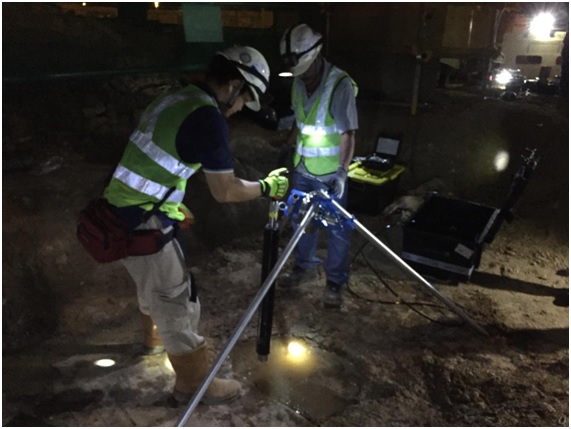
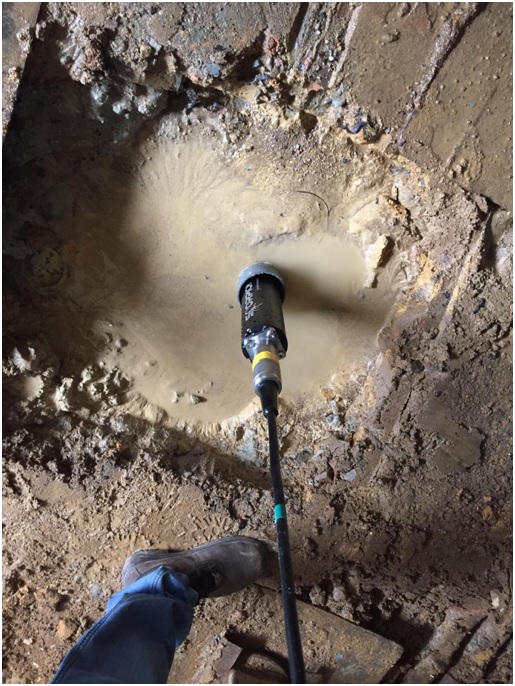
1. Crosshole Tomography
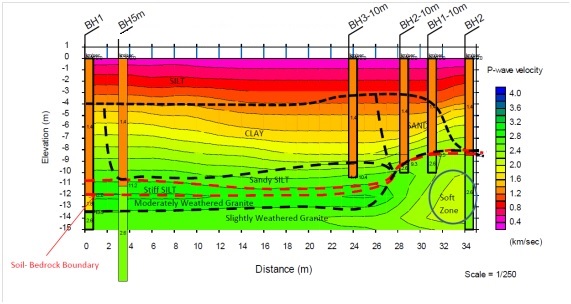
Crosshole tomographic measurements between boreholes or between boreholes and the ground surface can provide subsurface images superior to those based only on surface measurements. The boreholes separation minimum requirement is 20 meters.
Applications
• Delineate geological structures
• Specify mechanical soil and rock properties
• Map cavities and weak zones
Advantages
• Create higher resolution images
• Ability to image subtle targets



2. Parallel Seismic
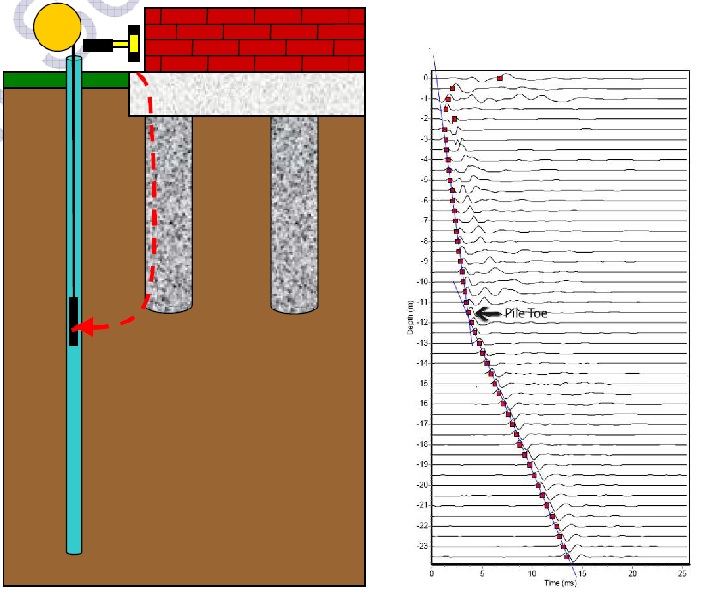
A very simple and effective method to determine the unknown or to confirm the depths of deep foundation, especially piled foundation. A borehole is drilled 0.5-1meter away from the foundation.
Applications
• Works well for columnar type of foundations, such as bored piles and caisson piles
• Provide depth of foundations made of concrete, wood, steel and masonry
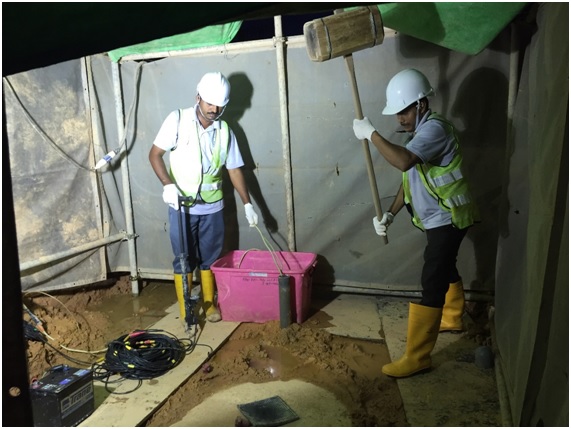


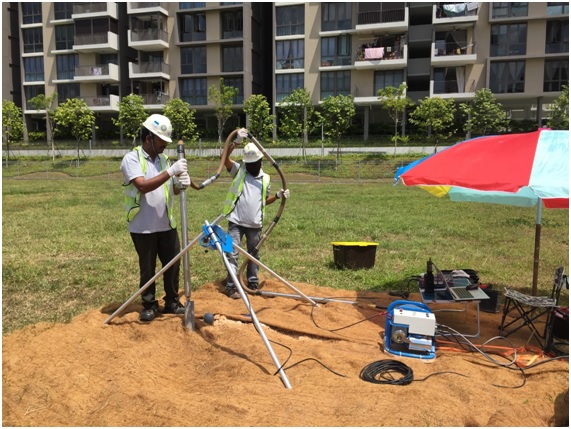
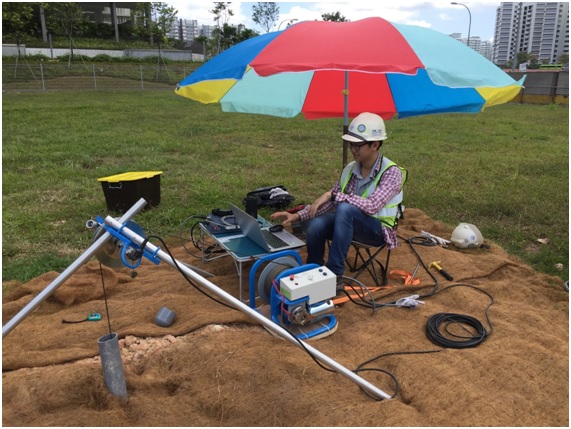
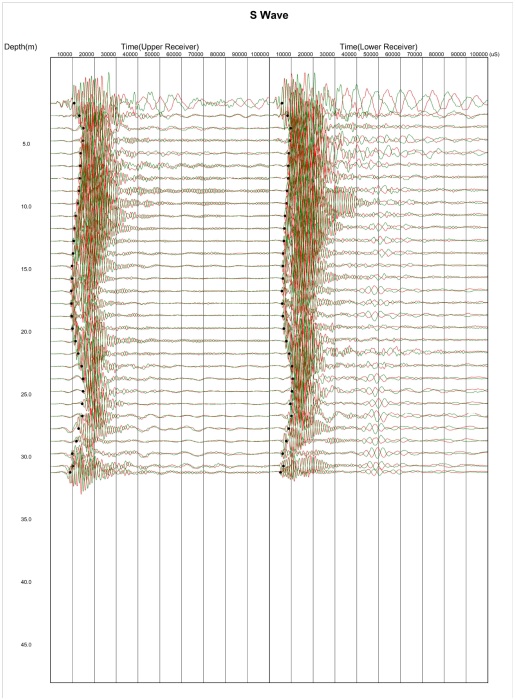
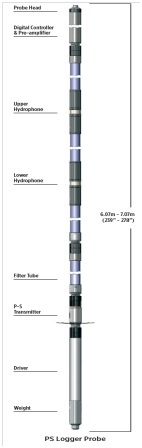
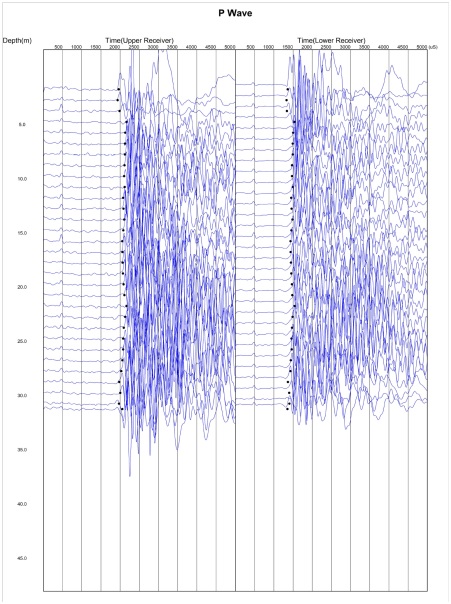
3. Suspension PS Logging
Suspension P-S logging test determines the shear and compression wave velocity (VS and VP) profiles in both soil and rock formations by using a 7-meter probe, containing hammer source and two receivers, separated by acoustic damping tubes. The reading is taken at every 1meter interval
Applications
• Site investigation – foundation studies, offshore structures, dam safety
• Physical properties of soil/rock – shear modulus bulk modulus, compressibility and Poisson’s ratio
• Earthquake engineering – characterization of strong motion sites