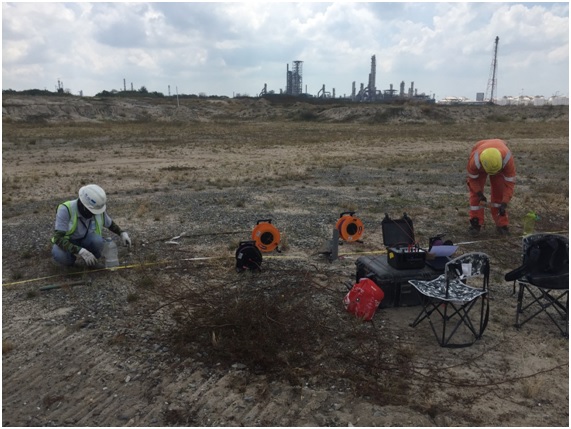
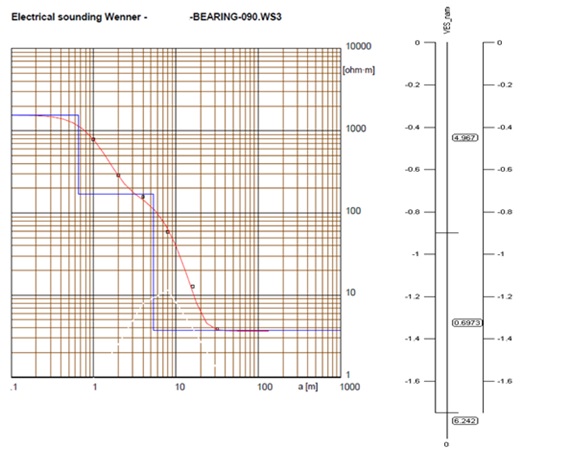
1. Vertical Electrical Sounding (VES)
The electricity flow in the soil is electrolytic and determined by the transport of ions dissolved in moisture. With the method of Resistivity test, the earth resistance, expresses in ohm-meter or ohm-centimetre, can be obtained and provide critical factor in electrical grounding design.
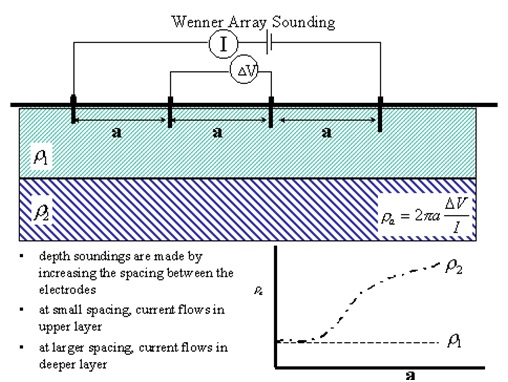
The common array use effectively for shallow vertical electrical sounding (VES) at one location is Wenner array. It consists of four electrodes which spacing between electrodes are varied accordingly. The four (4) electrodes need to spaced out at equal distances to approximate the depth of the soil to be tested.
Applications
- Delineation of aggregate deposits for quarry operations
- Measuring earth impedance or resistance for electrical grounding circuits or for cathodic protection
- Estimating depth to bedrock, to the water table, or to other geoelectric boundaries
- Mapping and detecting other geologic features
Limitations
Data quality will be compromised for work near long linear conductors such as buried gas metal pipelines, railroad tracks, rebar etc


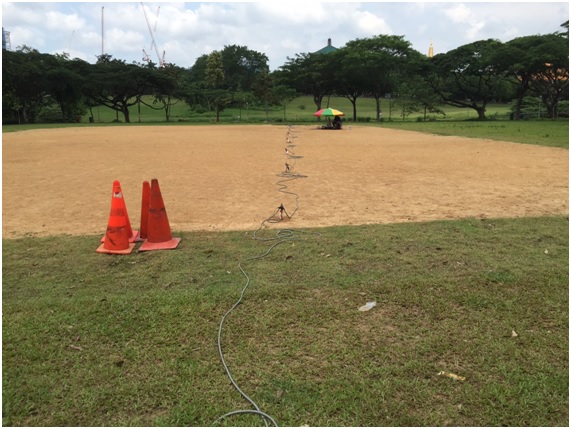
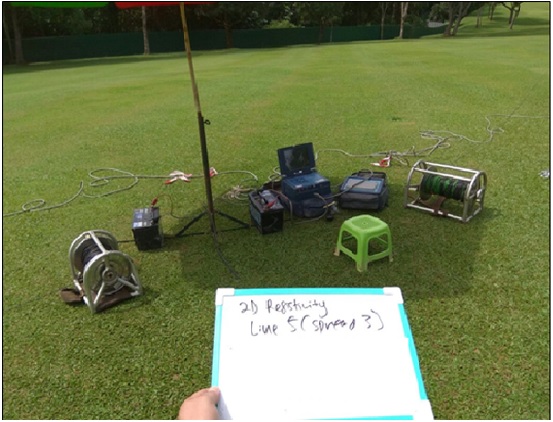
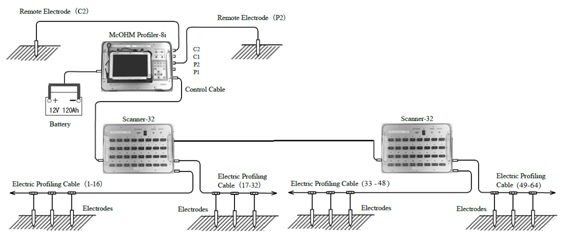
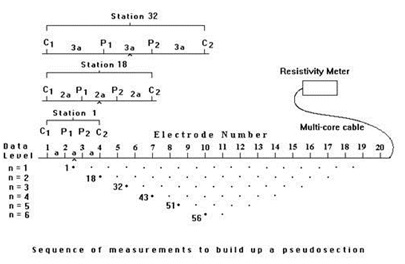
2. 2-D Resistivity Tomography
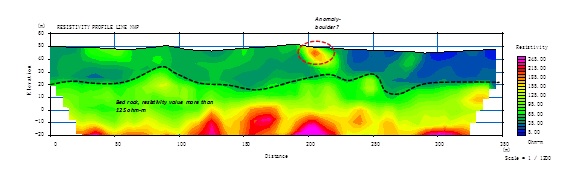
2-D Resistivity Tomography uses an array of 32 to 64 electrodes to develop a pseudosection with depth of variation in resistivity along the survey line. Depth and resolution of the investigation is determined by the spacing between the electrodes and the number of electrodes in an array.
Applications
- Map faults
- Map lateral extent of conductive contaminant plumes
- Locate voids and karsts
- Map heavy metals soil contamination
- Delineate disposal areas
- Mapping of Cavities & Sinkholes
- Explore for sand and gravel
- Mapping of Boulders


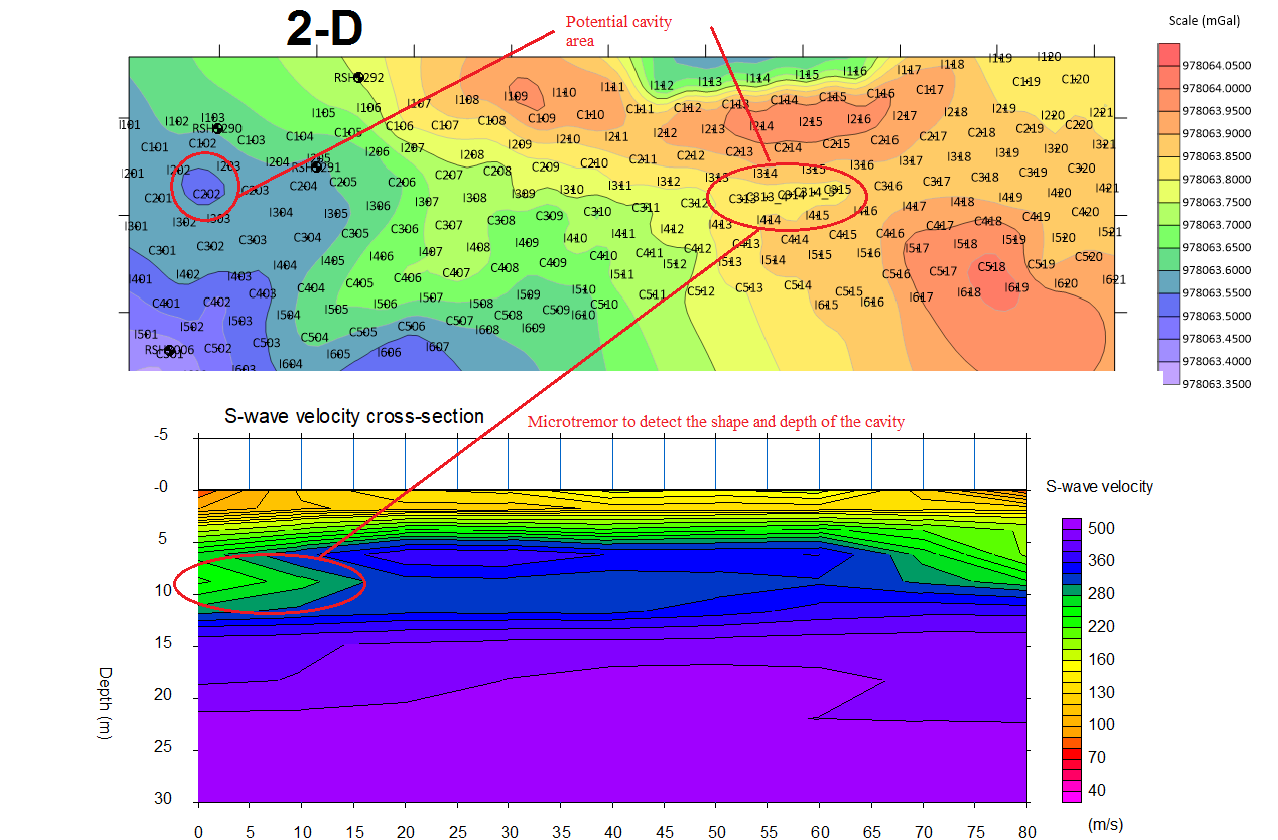
3. Microgravity Survey
The Microgravity technique in the context of civil engineering consists of measuring minute variations in the gravitational pull of the Earth and interpreting the presence of voids and cavities from these readings.
Applications
- Detection and delineation of subsurface cavities (karst conditions)
- Subsurface exploration for natural gas and oil
- Applied to any other substance that provides a density contrast from the rock or substance surrounding it. This means that minerals, ores, and other economically important substances can be detected
- Bedrock can be mapped, and lithologic changes and geologic structures can often be identified through proper modelling of gravity data